According to the American Stroke Association, stroke is the most frequent cause of long-term disability in the United States and the fifth-leading cause of death. Recent statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) showed that one in six deaths (17.5%) from cardiovascular disease was due to stroke, and more than 795,000 people in the U.S. have a stroke every year.
A stroke can significantly impair motor skills, language, cognition, and physical function. The good news is that we can optimize stroke recovery with the right protocols and the latest technologies applied early in the rehabilitation journey.
Let’s review what you need to know about stroke warning signs and side effects, why post-stroke rehab is essential, how stroke rehabilitation techniques facilitate recovery, the latest technologies that aid stroke rehab, and how patients can embark on a new beginning with proper stroke recovery protocols.
When you’ve had a stroke, you can be left with more questions than answers. We can help. This book pinpoints the essential information that will help you understand your situation and navigate each stage of your recovery.
Read below or fill out the form to download our free guide to start charting your course.
Click a link to go directly to a specific section.
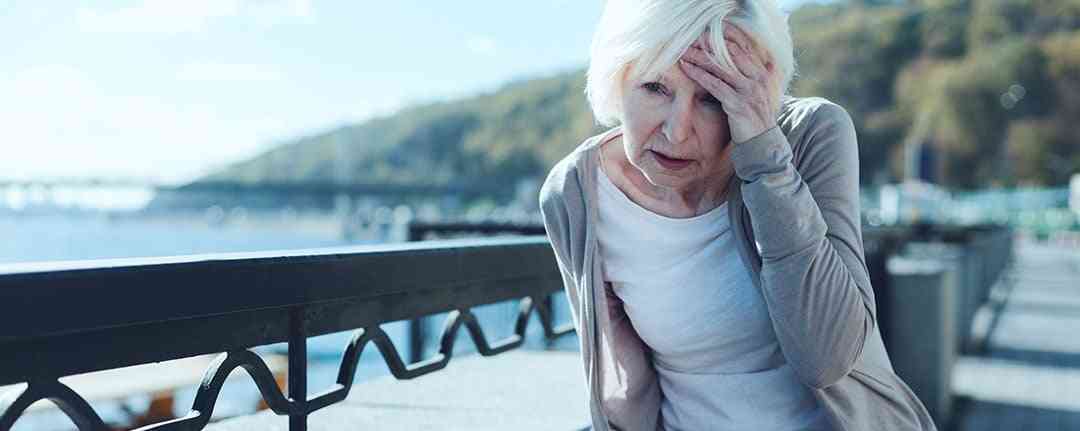

A stroke occurs when a vessel that supplies blood to the brain ruptures or becomes blocked, starving brain cells of oxygen and resulting in brain damage. When an area of the brain experiences a sudden reduction or loss of blood flow, the affected brain cells are deprived of oxygen and begin to die within seconds.
There are five types of strokes:
Knowing the early warning signs of a stroke is crucial because prompt medical treatment can significantly minimize brain damage, improve stroke recovery outcomes, and reduce the risk of long-term disability or death. Here are eight stroke warning signs to watch for:
Research suggests that women may experience additional, atypical, or less common stroke warning signs. These may include sudden hiccups, general weakness, chest pain, palpitations, shortness of breath, and behavioral changes.
Take immediate action if you or a loved one shows any combination of these stroke warning signs. Note the approximate time the first symptoms appeared and get emergency medical attention as quickly as possible.
Understanding what to expect after a stroke helps facilitate effective stroke recovery planning. Individuals can proactively manage risk factors and adjust their lifestyles by anticipating stroke side effects and potential challenges.
The most common physical stroke side effects include dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), fatigue, pain, spasticity, and vision impairment like partial blindness, tunnel vision, double vision, and blind spots.
Some patients may suffer from muscle impairment, such as hemiparesis (weakness on one side of the body), incontinence (the inability to control the bladder and/or bowel movements), foot drop (dragging one’s toes when walking), or paralysis (the inability to move muscles or muscle groups).
Moreover, the brain damage caused by a stroke can trigger seizures and/or epilepsy. Around 5% to 20% of patients experience a seizure after a stroke, with some developing chronic seizures and epilepsy.
Patients may also suffer from post-stroke depression and other emotional or mental stroke side effects.
 The stroke recovery timeline is unpredictable. Some patients may recover completely within weeks, while others may take months or even years to recover fully. Some patients may experience moderate to severe stroke side effects permanently.
The stroke recovery timeline is unpredictable. Some patients may recover completely within weeks, while others may take months or even years to recover fully. Some patients may experience moderate to severe stroke side effects permanently.
Several factors affect the stroke recovery timeline, such as the stroke's type, location, and severity. Additionally, the timeline may be shorter if the patient received prompt treatment immediately after the stroke.
Here’s an overview of a typical stroke recovery timeline:
While this stroke recovery timeline varies based on each patient’s circumstances, post-stroke rehab should be a critical part of this period to facilitate the healing process.
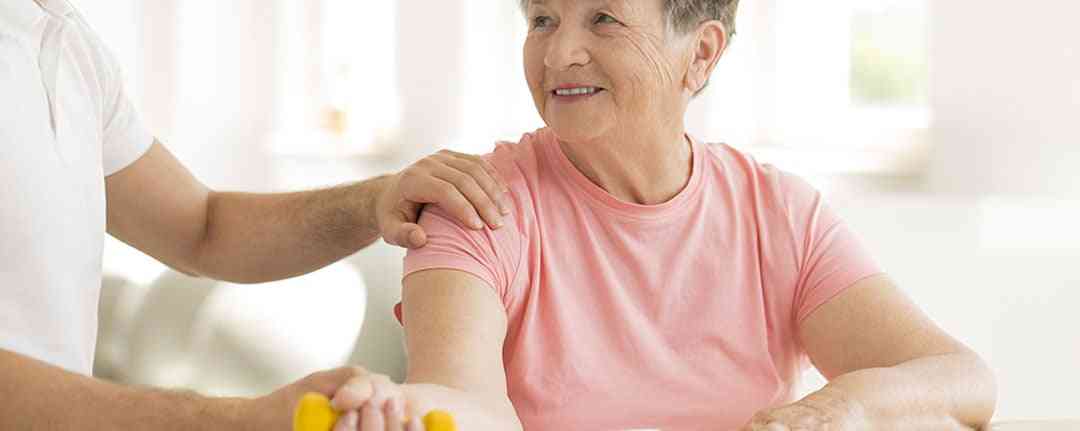

A well-designed rehabilitation program is critical to speeding up the stroke recovery timeline. It can improve physical outcomes and address long-term emotional and mental stroke side effects. Let’s explore why post-stroke rehabilitation is essential.
Post-stroke rehabilitation helps patients relearn the skills they lost due to the brain damage caused by the acute care episode. These may include coordinating leg movements to walk again or performing steps in a complex activity. Therapists also teach stroke survivors new ways to perform tasks to compensate for the loss of movement.
Some patients may lose their ability to speak and communicate after a stroke, while others may not be able to perform daily tasks like dressing or bathing. Post-stroke rehabilitation helps them regain these skills and their independence, which is essential for improving their quality of life and mental well-being.
Physical therapy is a form of rehabilitation treatment that focuses on rebuilding physical strength and mobility through a supervised and structured regime of exercises. Physical therapy treatment is an essential component of stroke recovery, and the first stage should begin in the hospital within one to two days of a stroke.
While stroke patients may experience natural recovery without rehab, evidence suggests that physical therapy for stroke patients helps facilitate better and faster stroke recovery. For example, physical therapy helps patients improve overall strength and mobility, prevent muscle atrophy, improve quality of life, regain independence, and overcome mental and emotional challenges like post-stroke depression.
 Brain injury caused by a stroke can cause post-stroke depression or exacerbate a patient's previous mental conditions. Individuals who have experienced a cerebellar stroke may face long-term depression. Ischemic strokes, caused by blockages in blood vessels supplying the brain, may also have long-term effects on mood and mental health.
Brain injury caused by a stroke can cause post-stroke depression or exacerbate a patient's previous mental conditions. Individuals who have experienced a cerebellar stroke may face long-term depression. Ischemic strokes, caused by blockages in blood vessels supplying the brain, may also have long-term effects on mood and mental health.
It’s not uncommon for patients to need psychiatric help after a stroke. Counseling and psychotherapy ("talk therapy") can help relieve post-stroke depression and facilitate stroke recovery. Some patients may also benefit from using antidepressants to help them recover from long-term stroke side effects.
Physical therapy and counseling, along with other techniques, play a critical role in stroke recovery. Let’s look closely at how they stabilize a patient’s condition, help them regain optimal function, and promote the best quality of life.
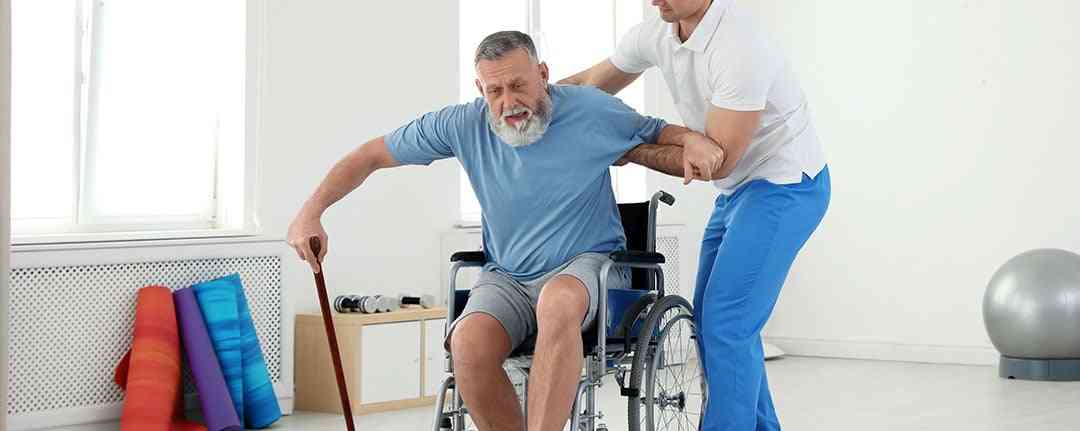
A stroke rehabilitation team often includes a physical therapist, occupational therapist, speech-language pathologist, social worker, neurologist, and other professionals to meet the diverse needs of stroke patients. They use different techniques to help facilitate the stroke recovery journey.
The majority of rehab facilities use these stroke rehabilitation techniques to help patients regain their functions and accelerate their stroke recovery journey:
Speech and language pathologists help patients recover their ability to communicate and swallow after a stroke. They also help improve patients' reading and writing skills. Techniques may include cadence and breathing exercises and word meaning and repetition practice.
An individualized physical therapy program helps stroke patients regain their physical function or compensate for physical deficits after a stroke, improving mobility and movement where there’s impairment. Therapists may also incorporate e-stimulation and other therapies into their treatment plans.
This stroke rehabilitation technique helps restore a patient’s ability to perform routine daily activities, such as cooking, driving, household chores, and grooming. An occupational therapist also helps patients overcome physical limitations, adjust their living spaces, avoid safety concerns, and improve their quality of life.
Neurological therapies encourage neuroplasticity to build new neural pathways and improve cognitive and motor impairments caused by brain and nerve damage from a stroke. Magnetic brain stimulation may help patients walk and move better, while brain exercises help sharpen cognitive function.
Mirror therapy addresses one-sided paralysis or weakness. The patient moves the unaffected limb and watches it in a mirror. The brain processes the movement in the mirror as if it happens to the affected limb. Many patients notice improvements in strength and mobility on the weak or paralyzed side.
This stroke rehabilitation technique helps patients return to activities they enjoy or learn new ones to improve mental well-being and health. Patients can also practice communication skills and physical abilities gained from physical and occupational therapies during these activities.
Speech and physical therapies are the most critical and impactful of these stroke rehabilitation techniques. Let's explore how they support stroke recovery.
The severity of injury from a stroke can impact the ability to communicate in multiple ways. For example, a stroke that affects the left side of the brain, which controls speech and language, may alter the patient’s ability to speak or understand what others say, leading to a condition called aphasia.
In speech therapy for stroke patients, therapists pinpoint the exact issues faced and develop a plan to address them — restoring language abilities where possible, working around remaining challenges, and devising other ways for patients to express themselves.
Speech therapy for stroke patients often includes breathing exercises, tongue and lip exercises, articulation coaching, voice training, and word and sentence articulation. These techniques aim to help patients regain communication abilities, modulate their voice, and recognize verbal cues.
To achieve the best outcomes, speech therapy for stroke patients should start as soon as possible.
Speech therapy helps stroke patients build communication skills for relationships, work, and everyday activities to regain independence and improve their quality of life. It also retrains swallowing skills to avoid choking issues, malnourishment concerns, and embarrassment associated with the inability to swallow.
Stroke reduces mobility in more than half of stroke survivors 65 and older. Physical therapy after stroke takes a diverse approach to addressing mobility challenges. It targets various aspects of recovery (e.g., physical, neurological, and functional) and each patient's unique challenges to achieve the best outcomes.
Mobility and gait training restores the ability to walk. A therapist may use parallel bars or treadmills to help patients relearn walking skills and introduce walking aids to support stroke recovery. Meanwhile, strength and flexibility exercises rebuild power and endurance while addressing stiffness to lower the risk of contractures (permanent tightening of muscles or tendons).
Physical therapy after stroke also involves balance and coordination exercises to help patients minimize the risk of falls. Functional retraining guides patients to practice essential daily activities, facilitating their return to normal life based on their lifestyle needs and recovery goals.
Chartered Society of Physiotherapy found that high-intensity stroke recovery exercises begun within 24 hours after a stroke can improve outcomes, helping patients regain mobility, strength, and independence.
Physical activities for stroke patients promote neuroplasticity by stimulating the brain to form new neural pathways and facilitate functional recovery. These treatments also help manage spasticity (muscle tightness) and improve muscle tone to minimize discomfort while aiding movement.
Physio for stroke patients goes beyond improving physical functions. Experiencing progress and achieving milestones boosts patient confidence while reducing anxiety and post-stroke depression, enhancing emotional well-being. As they regain functional independence, patients can also reintegrate into daily life and reengage with social activities.
 Here are the top stroke recovery exercises that aid the stroke recovery process:
Here are the top stroke recovery exercises that aid the stroke recovery process:
In addition to these tried-and-true stroke rehabilitation techniques, reputable rehab facilities provide access to the latest technologies to promote stroke recovery. Let’s review the latest advances and how they may help.

Breakthroughs in new stroke therapy help significantly improve stroke patients' quality of life and health outcomes. Here are the most pivotal advances in stroke recovery:
These advances in stroke recovery augment conventional stroke rehabilitation techniques to facilitate the rehabilitation journey:
This surgical procedure, performed up to 24 hours after a stroke, removes a blood clot from a blood vessel. It reduces the severity of stroke side effects for many patients and improves the likelihood that the patient will recover functional independence.
This treatment may facilitate stroke recovery for patients with impaired upper limbs. It involves implanting a medical device that delivers electrical impulses to the Vagus nerve, a long nerve that controls heart rate, peristalsis, sweating, and several muscle movements, to release neurotransmitters into the brain to strengthen synaptic connections.
This non-invasive procedure involves holding an electrode near a patient's head to send impulses through the brain. The high-frequency rTMS promotes functional recovery by inducing the brain's endogenous repair and recovery mechanisms.
Research published in the Journal of Stem Cells Translational Medicine found that a single infusion of umbilical cord blood was safe and helpful in treating ischemic strokes. Researchers theorized that umbilical cord blood might stimulate the development of new neuronal activity in stroke patients.
Reputable stroke rehab facilities often incorporate these technologies into personalized treatment plans to facilitate stroke recovery:
Using video games for stroke recovery is one of the new trends that helps patients regain full use of their limbs. Like other effective stroke rehabilitation techniques, video games for stroke patients help improve neuroplasticity. Such “rewiring,” supported by consistent exercise, helps patients recover lost functionalities.
Video games promote neuroplasticity by leveraging repetitive, engaging, and goal-oriented activities to stimulate the brain and facilitate healing. They also make it easier for patients to commit to performing repetitive movements through engaging tasks.
Video games for stroke patients, supported by virtual reality (VR) technology, offer multisensory stimulation (e.g., visual, audio, and tactile feedback). They help improve hand-eye coordination while activating multiple brain regions simultaneously to encourage the creation of new neural pathways.
Moreover, many video games require players to use both hands or coordinate actions between hands and feet, promoting communication between the brain's hemispheres. The cross-lateral stimulations help restore balance and function between the affected and unaffected sides of the body.
 Some video games for stroke patients also involve problem-solving, memory, and decision-making skills to support cognitive flexibility and strengthen neural networks. They also stimulate the release of dopamine — a neurotransmitter that strengthens synaptic connections and keeps patients motivated.
Some video games for stroke patients also involve problem-solving, memory, and decision-making skills to support cognitive flexibility and strengthen neural networks. They also stimulate the release of dopamine — a neurotransmitter that strengthens synaptic connections and keeps patients motivated.
Today, reputable rehab facilities combine cutting-edge gaming technologies with traditional stroke rehabilitation techniques to maximize the benefits of video games for stroke patients.
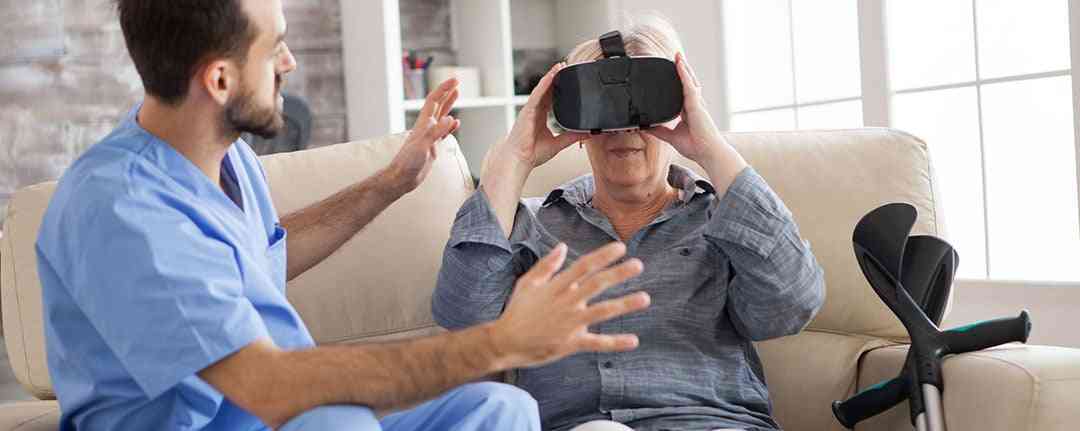

Stroke recovery is a long journey. Life after stroke requires a lot of adjustments. The good news is that many patients can take their lives back through effective therapy supported by hard work, determination, and patience.
Therapy is an essential part of life after stroke to help you recover from the event and lower the risk of having another one. Your rehabilitation team will help you regain strength, relearn lost abilities, and work around disabilities or weaknesses. They will also help you manage the emotional side effects, such as post-stroke depression and anxiety.
Here are a few pointers to navigating life after stroke:
Inpatient stroke rehab involves checking into a specialized rehabilitation facility for intensive therapy and care. Outpatient rehabilitation therapy may consist of appointments at a rehabilitation clinic daily or several times per week or having therapists provide services in your home.
Your doctor can help you make the best decision for your care. However, during the first few weeks after stroke, many patients — especially those who experience significant impairments — benefit most from round-the-clock professional attention and intensive rehabilitation programs in dedicated, inpatient rehab centers.
Stroke survivors who begin rehabilitation therapy as soon as they're medically stabilized and get permission from their doctors accomplish the most progress. They recover more skills, abilities, and strength than those who delay rehab or fail to continue therapy.
About 185,000 strokes per year, nearly one in four, happen in people who have had a previous stroke. Managing modifiable risk factors for stroke through dietary and lifestyle changes can help lower your risk for another stroke and improve your overall health.
Modifiable risk factors for stroke include high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, high cholesterol, a sedentary lifestyle, being overweight, poor diet, excessive alcohol consumption, heart disease, arteriosclerosis, and chronic stress.
Here are some tips to manage modifiable risk factors for stroke:
The good news is that you don’t have to embark on your stroke recovery journey alone. The right stroke rehab facility can provide the appropriate support to help you navigate the process to achieve the best outcomes.
The American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation estimates that 55% of stroke patients require inpatient care after their initial hospitalization to help them recover.
Inpatient rehab facilities like Rehab Select use evidence-based approaches to design personalized treatment plans for stroke patients to meet individual needs while providing patients with round-the-clock, multi-disciplinary, specialized stroke care.
The intensive nature of this approach ensures patients stay on track with their treatments to shorten the stroke recovery timeline. All the specialists and caretakers communicate regularly to stay on the same page and support each other’s therapy regimens.
Moreover, staff members in inpatient rehab facilities are knowledgeable about community programs and other resources patients may need when they return home, such as medical specialists, in-home help, and support groups, to support their long-term stroke recovery.
Stroke recovery may take place in several types of rehab settings after a patient is discharged from the hospital:
Choosing the best stroke rehab facility for your needs can be overwhelming. Here are some questions to ask when selecting one for you or your loved one:
Questions for your insurance provider:
Questions for the stroke rehab facility:
 How do they prevent reoccurring strokes?
How do they prevent reoccurring strokes?Besides asking these questions, seek a stroke rehab facility that aims to get patients home as quickly as possible. They should prioritize each patient’s quality of life and help restore their self-confidence and autonomy. They should build their rehab programs to support real-life needs and help you plan the discharge process diligently to make returning home as easy and stress-free as possible.
The American Stroke Association recommends that patients who have suffered a serious stroke participate in intensive inpatient rehab for as long as possible.
Rehab Select’s five state-of-the-art facilities across Alabama are here to help. We provide access to a team of specialists who facilitate stroke recovery with a personalized treatment plan, various therapeutic modalities, and new technology for stroke patients —helping patients shorten their stroke recovery timeline.
Learn more and schedule a tour of our facilities in Alabaster, Talladega, Montgomery, Albertville, or Guntersville.
